The term trickle charge is a process that helps maintain a battery’s charge to its full potential. It’s typically used to prolong the life of a battery while it’s not being used. When referring to this type of method, could a product like a DIN rail power supply be used, such as part number DRC-100A?
Image of DRC-100A
The answer is yes, it can be used for this process, but there are a few things to consider for this type of application. Let’s take a look at some of the attributes this product has to offer for charging:
- Power supply with battery charger/UPS function.
- Charger output channel is 13.8V with 2.5A of current for the battery charging side.
- It also features battery-low protection and reverse polarity protection, which shows it can be paired with a battery for backup.
The UPS (uninterruptible power supply) feature provides backup power when an AC outage occurs. This function makes sure devices sustain power so they can continue to operate until the AC power is restored.
If you plan on using this type of product for the application, below are some categories/attributes that need to be evaluated.
Battery Chemistry
- Each chemistry has very different charging profiles, such as lead-acid and Li-ion.
- The spec 13.8V is typically used for 12V lead-acid systems, as this is a common trickle voltage for this type.
Voltage Info
- If you are using a 12V lead-acid type battery, a trickle voltage around 13.8V should work. However, always check the battery manufacturer’s documentation to see if it will handle this voltage, before applying this in your design. The snip below is an example of the datasheet information in regard to charge voltage:
Current Control
- The charger portion is rated for 2.5A of current. If the battery has a smaller Amp hour rating, it’s possible that it could over-charge unless the circuit consists of limiting the additional current, or the battery has internal regulation.
- If the battery is disconnected often or you leave it connected constantly, you need to make sure the charger doesn’t switch into “bulk” mode, which may overcharge the battery.
Compatible Examples
Below is a list of examples that are compatible in using this type of charging method.
Applications
When using DRC-100A, MEAN WELL suggests using this product for a backup connection for AC interruption and an alarm signal for “AC OK” and “battery low” applications. Some examples of these applications are listed below:
- Security/Alarm Systems - Alarms and sensors will stay running if AC power is lost.
- Emergency Lighting - Maintains lighting circuits until AC power is restored.
- Building Automation - Reliable power source that doesn’t drop out (fall below the expected DC voltage level).
- Door Entry Systems - Locks remain powered during a power outage.
Another Note
If a slightly higher or lower voltage is required for this type of charging method (with the means of staying around 12-15V on the adjustment range for this product), you can adjust the voltage using the following method:
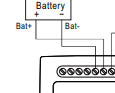
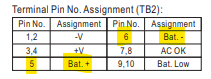
- Using the leads from a multimeter (0-20V DC setting), measure the DC output on the power supply’s terminals that are isolated for the battery connection (Pin 5 Bat.+, Pin 6 Bat.-).
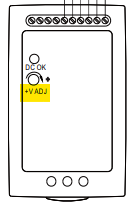
- Use a small screwdriver to adjust the voltage, it should be labeled “V ADJ”:
- Turning it to the right will increase the voltage and turning it to the left will lower it.
- After each adjustment, let the voltage stabilize for a few seconds before measuring again.
If you are not familiar in using a multimeter, we also have a video that shows how to use them in the following:
More info about using AC to DC converters as battery chargers - Can an AC to DC converter be used to charge a battery?
Datasheet Location: DRC-100 Series Datasheet