The Arduino Uno WiFi and Arduino Nano R4 both feature a 32-bit Renesas RA4M1 processor configured for 5 VDC input and output voltages. This is an excellent feature for the Arduino community as it provides backward compatibility with previous UNO generations (shields and circuit still work).
What is the Arduino Qwiic Voltage?
The Arduino UNO R4 WiFi and the Arduino Nano R4 provide 3.3 VDC for the Qwiic.
-
The RA4M1 microcontroller operates at 5 VDC.
-
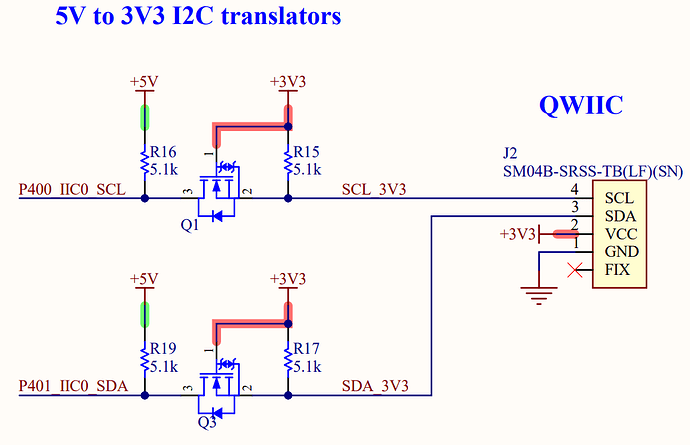
Level shifters are used to interface the microcontroller to the Qwiic devices. Figure 1 presents the circuit for the Arduino Nano R4.
-
The Qwiic power pin is derived from a 3.3 VDC regulator.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram for the Arduino Nano R4 Qwiic circuitry showing 3.3 VDC level shifters.
How much current can the Arduino UNO R4 WiFi supply to the Qwiic devices?
The short answer is about 200 mA.
To date, I have not found the official Arduino specification. However, we can reverse-engineer the design to support the 200 mA estimate.
Heat Dissipation from the Linear Regulator
The Arduino UNO R4 WiFi uses a SGM2205 linear voltage regulator rated for 800 mA. We would be negligent if we used this value without considering the heat dissipation in this SOT-223 packaged regulator.
Calculate the power dissipation as:
V_{Drop} = 5 - 3.3 = 1.7
P_{Dissipation} = V_{Drop} \times Current
-
Evaluation at 800 mA, the regulator dissipates approximately 1.4 W.
-
Evaluation at 200 mA, the regulator dissipates approximately 0.4 W.
Note that the SOT-223 package has a thermal rating of 95 ℃/W with an ideal 1.32 W dissipation. Here “ideal” implies that we can keep the junction temperature at +25℃. That’s nearly impossible unless the Arduino operates in arctic conditions.
From this analysis, we conclude that it is better to keep the current low to prevent excessive heat dissipation and thermal shutdown of the regulator.
Tech Tip: Excessive Qwiic current can cause the regulator to cycle on and off about the thermal setpoint. You can test for thermal shutdown using a can of compressed air. Invert the can and slowly apply a drip of the condensed liquid to the regulator.
The Arduino UNO R4 WiFi Qwiic supply is fused
A 500 mA resettable Bourns MF-MSMF050 PTC fuse is used to protect the linear regulator.
How much current can the Arduino Nano R4 supply to the Qwiic devices?
The short answer is about 150 mA.
The Arduino Nano R4 uses a Diodes Incorporated AP2112K-3.3TRG1 linear regulator to supply the Qwiic connected devices. While this part is capable of providing 600 mA, it can only do so while dissipating a large amount of heat. This quote from the Arduino Nano R4 datasheet suggests 150 mA is the design maximum:
When using the 3V3 pin to power external peripherals, notice that above 150 mA the board may become very hot due to LDO regulator functioning basis.
Note that the Arduino Nano R4 Qwiic connection is unfused. I suspect the fuse couldn’t be fitted on the exceptionally compact PCB.
![]() Article by Aaron Dahlen, LCDR USCG (Ret.), Application Engineer at DigiKey
Article by Aaron Dahlen, LCDR USCG (Ret.), Application Engineer at DigiKey