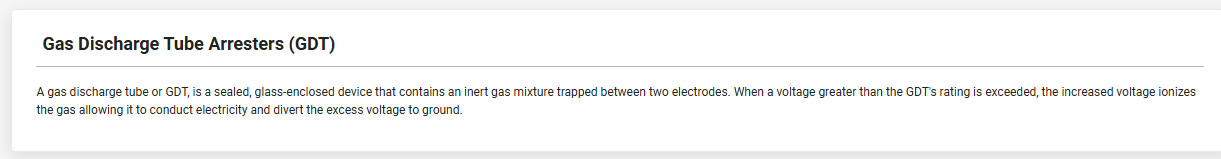
Lightning arresters are also called Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs). Gas discharge tubes (GDTs) are sealed glass-enclosed devices with an inert gas mixture injected between two electrodes. When the voltage exceeds the rated value of the GDT, the increased voltage ionizes the gas, making it conductive and transferring the excess voltage to the ground.
What are the key performance specifications we should use to choose the right lightning arrester?
- DC Spark-over Voltage (DC Breakdown Voltage)
- Maximum Impulse Spark-over Voltage (Pulse Breakdown Voltage)
- Nominal Impulse Discharge Current
- Impulse Life
When making your selection, pay attention to the difference between DC breakdown voltage and pulse breakdown voltage. The selection of DC breakdown voltage should refer to the working voltage of the circuit. The DC breakdown voltage should be greater than the maximum working voltage of the protected circuit, otherwise it will affect the normal operation of the circuit.
The pulse breakdown voltage should consider the surge test level. The rise time of the general surge test waveform is a microsecond pulse waveform, such as 8/20μs current wave and 10/700μs voltage wave, which is an order of magnitude modified by the GDT pulse breakdown voltage measurement voltage rise rate of 1000V/μs. For example, if a 10/700μs waveform is used to test 4000V, the pulse breakdown voltage of the GDT must be less than 4000V, so that the GDT can be turned on during the test.
Choose the appropriate form factor/package according to the circuit design layout. The size of the GDT device package can reflect the device’s protection level to a certain extent. Generally, the larger the GDT, the stronger the device’s ability to withstand impact current and the higher the protection level, and vice versa.