This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the Thyristors - TRIACs category on DigiKey.com
Thyristors conduct AC (alternating current) in one direction or one half of an AC cycle. A TRIAC (triode AC) conducts current in either direction when its gate is triggered. Other names include bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor. TRIAC types are snubberless, alternistor, internally triggered, logic gate and standard which are chassis, surface or through-hole mount. Selection is by off state voltage, on state current, hold current and gate trigger voltage.
SelectionCharacteristics
Specifications to determine which TRIAC is right for your application.
TRIAC Type: Indicates grouping of a device among one of several sub-classes of TRIACs, differentiated by triggering characteristics and commutation performance.
Voltage - Off State: Indicates the maximum instantaneous voltage that may be repetitively/continuously applied to a device in a non-conducting state without causing damage.
Current - On State (It (RMS)) (Max): The rated maximum RMS (root mean square) current carrying capacity of a device, typically specified for sinusoidal current waveforms at 50/60 Hz.
Voltage - Gate Trigger (Vgt) (Max): The maximum voltage required to produce the listed gate trigger current. Measured under manufacturer-defined test conditions.
Current - Non Rep. Surge 50, 60Hz (Itsm): The maximum current a device is rated to conduct for a single half-cycle of an AC waveform of a specified frequency. Values shown for 50 and 60 Hz, or as indicated.
Current - Gate Trigger (Igt) (Max): The maximum current that must be passed through a device’s gate terminal to guarantee a device will trigger into conduction. Measured under manufacturer-defined test conditions.
Current - Hold (Ih) (Max): Characterizes the minimum current flow through a device required to maintain a conductive state.
Configuration: Identifies whether it is a single or array configuration.
Operating Temperature: Recommended operating temperature, typically given in a range or as a maximum. Exceeding these temperatures may affect performance or damage the device and other system components.
Mounting Type: Indicates how the device is attached.
Available Mounting Types
Chassis Mount
Designed to be mounted to a metal chassis.
Chassis, Stud Mount
Designed to be mounted to a metal Chassis using an incorporated stud bolt.
Stud Mount
Has a stud bolt incorporated into one side for attachment.
Surface Mount
Have pins or pads that connect to solder pads on the PCB that are then soldered in place forming an electrical and mechanical connection. Number in front of SMD indicates how many pins/pads, for example a 6-SMD module has 6 pins/pads. May not use or even have all the pins/pads for example 24-SMD module, 14 leads: would fit in the space of a 24-SMD module but only has 14 pins/pads. Typically, they are smaller than the through-hole components.
There are three basic types of pins (leads) for surface mount devices.
Lead Types
Gull wing leads: Enable the most pins per inch when compared to J-lead types but they are more fragile. Easy to inspect for defects after soldering.
![]()
J-Leads: Less pins per inch than gull wing leads but they are stronger and less susceptible to breakage.
![]()
Flat Leads: Must be protectively packaged to prevent damage to leads. Leads must be formed into a gull shape prior to use with a separate piece of equipment. Due to that they are the least popular type of lead.
![]()
Through-hole
Have leads that go through a pre-drilled hole on a PCB and are soldered in place forming both an electrical and a mechanical connection.
Package / Case: Indicates the type of protective case used on an electronic component to allow easy handling, installation, and protection. This selection was determined to be the closest industry standard applicable to the suppliers device packaging. Typically it is best to check the actual dimensions from the datasheet rather than depend on this terminology when designing your circuit.
Supplier Device Package: This is what the manufacturer calls the package of this device. They are manufacturer specific. It is typically best to use the actual dimensions from the datasheets rather than to go by this terminology when designing your circuit.
ProductExamples
| MFR PART # | TG40E60 |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | 4076-TG40E60-ND |
| MANUFACTURER | SanRex Corporation |
| DESCRIPTION | TRIAC Standard 600 V 40 A Chassis Mount |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
| MFR PART # | Z0103MNT1G |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | Z0103MNT1GOSTR-ND - Tape & Reel (TR) |
| MANUFACTURER | Littelfuse Inc. |
| DESCRIPTION | TRIAC Logic - Sensitive Gate 600 V 1 A Surface Mount SOT-223 |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
| MFR PART # | T2550-12T |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | 497-14585-5-ND |
| MANUFACTURER | STMicroelectronics |
| DESCRIPTION | TRIAC Alternistor - Snubberless 1.2 kV 25 A Through Hole TO-220 |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
Schematic Symbol
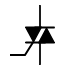

TRIAC schematic symbols courtesy of Scheme-It please use the link for more information and symbols.
MediaLinks
Videos
Triacs - NXP Semiconductors Quick Learning 3
Solid State Relays with TRIACS vs Electromechical Relays for three phase motor control
Power Factor Corrected TRIAC Dimmable LED Driver Solution
230VAC, 5W Buck-boost for TRIAC dimming - LV5011MD2GEVB
Articles
Dimming LEDs with Traditional TRIAC Dimmers
Articles on TRIACs
Product Training Modules
AC Switches Family, Part One - STMicroelectronics
AC Switches Family Part Two - STMicroelectronics
TechForum
TechForum posts on TRIACs



