Class 2 and Class II power supply differences are significant and important to understand.
-
Class 2, as identified by the NEC (National Electric Code), refers to the output voltage and power capabilities of ac-dc supplies.
-
Class II, as designated by the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), pertains to a power supply’s internal construction and electrical insulation.
Class 2
NEC Class 2 Output Voltage and Power
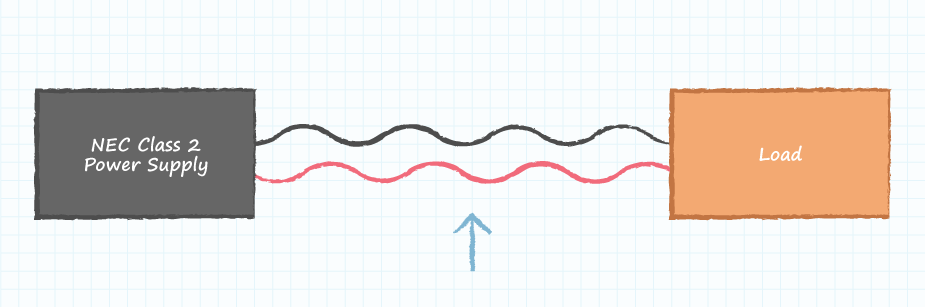
The NEC designation of Class 2 is important when installing an electrical system in a building. Class 2 power supply regulations address the wiring requirements (wire size and insulation, wire derating factors, overcurrent protection limits and methods of wiring installation) between the output of the supply and the input of the load. The limited output voltage and power delivery capabilities of Class 2 power supplies are recognized to be of lower risk to fire initiation and causing electrical shocks, which allows for lower cost wiring methods to be employed.
The UL Class 2 Power Units standards apply to power supplies within a limited output current and output voltage range. The Class 2 standard is specified in UL Standard Number UL1310. In order to receive the UL Class 2 approval, the power supplies must pass UL testing as follows:
The output current does not exceed 8 A.
The output voltage does not exceed 30 VDC.
Furthermore, a benefit of using the power supplies that have received the Class 2 approval is that the output has the same Class 2 safety level. When applying for safety standards approval for the equipment, in some cases it is not necessary to obtain safety standard approval for the connected device (load) when the device (load) is connected to the output of a power supply that has received Class 2 approval.
*Wiring affected by NEC Class 2 power supply
Class II
IEC Class II Insulation Protection
The IEC protection classes govern the construction and insulation of power supplies to protect the user from electrical shock. In a Class II power supply, there are two layers of insulation (or a single layer of reinforced insulation) between the user and the internal current carrying conductors. In supplies designed with two layers of insulation, the first layer of insulation is typically referred to as “Basic Insulation.” A common example of basic insulation is the insulation present on wires. The second layer of insulation is often an insulating case enclosing the product, such as the plastic case present on wall mount and desktop power supplies.
*Label showing the IEC protection Class II symbol (“Dual Walled” or “Double Insulated”)
IEC protection Class II power supplies will have a two-wire power cord as opposed to a three-wire power cord with Safety Earth connection. Products designed with Class II insulation often are labeled as “Class II” or “double insulated” or will have the concentric square symbol on the safety label.
Understanding the difference between NEC Class 2 and IEC Class II designated power supplies is a simple, yet important factor in ensuring the correct products are specified in user applications. Ultimately, by selecting a Class 2 or Class II certified power module, you are better protecting your design against electric shock and other hazards and failures that may occur.
DigiKey Website “Class 2” Search Tech Tip:
NEC Class 2 is part of the UL1310 standard, and since our website does not currently list "Class 2’’ as a filter option, by typing “1310” into the mini “Search Within” box can render you the 1310 UL standard:

Or, if you prefer you can manually highlight all 1310 options under the “Standard Number” filter:

See also:
Additional Info: Belfuse / Signal Transformer: Class-vs-Class
AC DC Desktop, Wall Adapters
Understanding the Five Transformer Types
Class I & Class II Wall Adapter Inputs
Transformer Insulation Class
Source ~ CUI INC
Source ~ OMRON