This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the Discrete Semiconductor - Transistors - Single FETs, MOSFETs category on DigiKey.com
Single FETs, MOSFETs - Discrete Field Effect Transistors (FETs), and Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) are widely used in power conversion, motor control, solid-state lighting, and other applications where their characteristic ability to be switched on & off at high frequencies while carrying substantial amounts of current is advantageous. They are used almost universally for applications requiring voltage ratings of a few hundred volts or less, above which other device types such as IGBTs become more competitive.
SelectionCharacteristics
Specifications to determine which FET/MOSFET is right for your application.
FET Type: FET channel type; influences the polarity of voltages applied to the device in typical use.
Technology: Identifies the semiconductor composition of the device.
Available Technologies
GaNFET
Cascode Gallium Nitride FET
GaNFET
Gallium Nitride FET
MOSFET
Metal Oxide FET
SiC
Silicon Carbide
SiCFET
Silicon Carbide FET
Drain to Source Voltage: The absolute maximum voltage between drain and source terminals that a device is rated to withstand. Magnitude of manufacturer’s ratings shown.
Current - Continuous Drain (ID) @ 25°C: Manufacturer’s indicated maximum drain current(s), subject to maintenance of a case (Tc) or ambient (Ta) temperature of 25°C. Allowable values in practice are subject to thermal limitations and may be much less than those indicated.
Drive Voltage (MAX rds On, Min Rds On): Indicates the gate-source voltage(s) at which the device’s on-state resistance is numerically characterized by the manufacturer.
Rds On (Max) @ Id, Vgs: The manufacturer’s specified maximum on-state drain-source resistance measured under the indicated test conditions. See datasheets for applicable thermal test conditions.
Vgs(th) (Max) @ Id: Characterizes the magnitude of the gate-source voltage at which a device turns “on” sufficiently to allow a drain current of the indicated magnitude to flow.
Gate Charge (Qg) (Max) @ Vgs: Characterizes the amount of electrical charge required to change an applied gate-source voltage from zero to the value shown, under manufacturer-defined test conditions.
Vgs (Max): The maximum voltage that may be applied across the gate and source terminals of a device without causing damage.
Input Capacitance (Ciss) (Max) @ Vds: Characterizes the sum of a device’s parasitic gate-to-drain and gate-to-source capacitances, measured at the indicated value of drain-source voltage.
FET Feature: Indicates distinguishing aspects of device construction or operating characteristics.
Available Features
Current Sensing
Modern power MOSFETs comprise thousands of identical transistor cells connected in parallel to minimize the overall on-resistance (RDS(ON)). A current-sensing MOSFET uses a small portion of these parallel cells to form a second low-power MOSFET (also called a senseFET) that is isolated from the power device, having a common gate and drain but a separate source that is brought out as a SENSE pin. For more information on current sensing please visit How to Select and Apply Smart Current Sensing and Monitoring Technologies
Depletion Mode
Indicates the device will be on in a zero gate-source voltage state.
Logic Level Gate, 4V Drive
Indicates the device can be driven with typical logic level voltage of 4-5V used by many integrated circuits (ICs).
Schottky Diode (Body)
Incorporates a Schottky Diode to prevent the device from reaching saturation, this enables faster switching times.
Schottky Diode (Isolated)
Includes a Schottky Diode but it is separate from the device, not incorporated into it like the body diode.
Standard
Temperature Sensing Diode
Incorporates temperature sensing technology and typically clamps the current when a certain temperature is reached to prevent over-temperature situations.
Power Dissipation (Max): Characterizes the amount of electrical power dissipation in a device that produces a specified internal device temperature (often the rated maximum) under specified operating conditions.
Operating Temperature: Recommended operating temperature, typically given in a range or as a maximum. Exceeding these temperatures may affect performance or damage the device and other system components.
Mounting Type: Indicates how the device is attached.
Available Mounting Types
Chassis Mount
Mounts to a metal chassis.
Surface Mount
Have pins or pads that connect to solder pads on the PCB that are then soldered in place forming an electrical and mechanical connection. There are three basic types of pins (leads) for surface mount devices.
Lead Types
Gull wing leads: Enable the most pins per inch when compared to J-lead types but they are more fragile. Easy to inspect for defects after soldering.
![]()
J-Leads: Less pins per inch than gull wing leads but they are stronger and less susceptible to breakage.
![]()
Flat Leads: Must be protectively packaged to prevent damage to leads. Leads must be formed into a gull shape prior to use with a separate piece of equipment. Due to that they are the least popular type of lead.
![]()
Surface Mount, Wettable Flank
A wettable flank is calling out a specific design in which the mounting edge of an IC has a fillet that allows you to see and test that a proper connection has been made on a pad that is for the most part not visible once soldered on a board. This aids in inspecting packages such as QFNs.
Through-hole
Have leads (pins) that go through a pre-drilled hole on a PCB and are soldered in place forming both an electrical and a mechanical connection.
Supplier Device Package: This is what the manufacturer calls the package of this device. They are manufacturer specific. It is typically best to use the actual dimensions from the datasheets rather than to go by this terminology when designing your circuit.
Package/Case: Indicates the type of protective case used on an electronic component to allow easy handling, installation, and protection. This selection was determined to be the closest industry standard applicable to the suppliers device packaging. Typically it is best to check the actual dimensions from the datasheet rather than depend on this terminology when designing your circuit.
ProductExamples
| MFR PART # | EPC2036 |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | 917-1100-2-ND - Tape & Reel (TR) |
| MANUFACTURER | EPC |
| DESCRIPTION | N-Channel 100 V 1.7A (Ta) Surface Mount Die |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
| MFR PART # | SCT3080ALGC11 |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | SCT3080ALGC11-ND |
| MANUFACTURER | Rohm Semiconductor |
| DESCRIPTION | N-Channel 650 V 30A (Tc) 134W (Tc) Through Hole TO-247N |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
| MFR PART # | IXFN180N15P |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | IXFN180N15P-ND |
| MANUFACTURER | IXYS |
| DESCRIPTION | N-Channel 150 V 150A (Tc) 680W (Tc) Chassis Mount SOT-227B |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
| MFR PART # | NTMTSC1D6N10MCTXG |
|---|---|
| DIGIKEY PART # | 488-NTMTSC1D6N10MCTXGTR-ND - Tape & Reel (TR) |
| MANUFACTURER | onsemi |
| DESCRIPTION | N-Channel 100 V 35A (Ta), 267A (Tc) 5.1W (Ta), 291W (Tc) Surface Mount, Wettable Flank 8-TDFNW (8.3x8.4) |
| DATASHEET | Click Here |
Schematic Symbol
N-CH ENH 1-----------P-CH ENH 1------N-CH DEP 1-------P-CH DEP 1-------N-CH ENH 2





P-CH ENH 2----------N-CH DEP 2-------P-CH DEP 2-----N-CH DUAL GATE, DEP 1—N-CH ENH 3





P-CH ENH 3------------N-CH DEP 3----------P-CH DEP 3---------N-CH ENH 4---------P-CH ENH 4





N-CH DEP 4------------P-CH DEP 4----------N-CH DUAL GATE, DEP 2-----P-CH DUAL GATE, DEP 1




P-CH DUAL GATE, DEP 2----MOSFET P-CHANNEL-----MOSFET N-CHANNEL
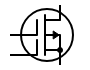


Schematic symbols courtesy of Scheme-it. Please see their website for more information and symbols.
MediaLinks
Videos
MOS FET Relays Introduction
Quick Learning: How to read a GaN FET datasheet
Videos on FETs and MOSFETs
Articles
The Significance Intrinsic Body Diodes MOSFETs
GaN FETs Improve Power Density and Efficiency
Articles on FETs and MOSFETs
How to Select and Apply Smart Current Sensing and Monitoring Technologies (Instead of Fuses)
Product Training Modules
Second Gen Lead Free eGaN® FETs
Product Training Modules on FETs and MOSFETs
TechForum
FETs (Field-Effect Transistors)
MOSFET Switch
TechForum Posts on FETs and MOSFETs




